Estimated Position (EP)
The approximate location of a vessel determined by dead reckoning, and accounting for external factors such as wind (Leeway) and Tide.
An Estimated Position (EP) is a concept in marine navigation, especially when precise fixes, such as those derived from celestial observations or GPS, are unavailable. The EP is calculated based on the vessel’s last known position, or fix, and factors in the course steered, the speed of the vessel, and the time elapsed since the last fix. It also considers external influences like wind, current, and tidal effects, which can cause the vessel to drift from its intended course.
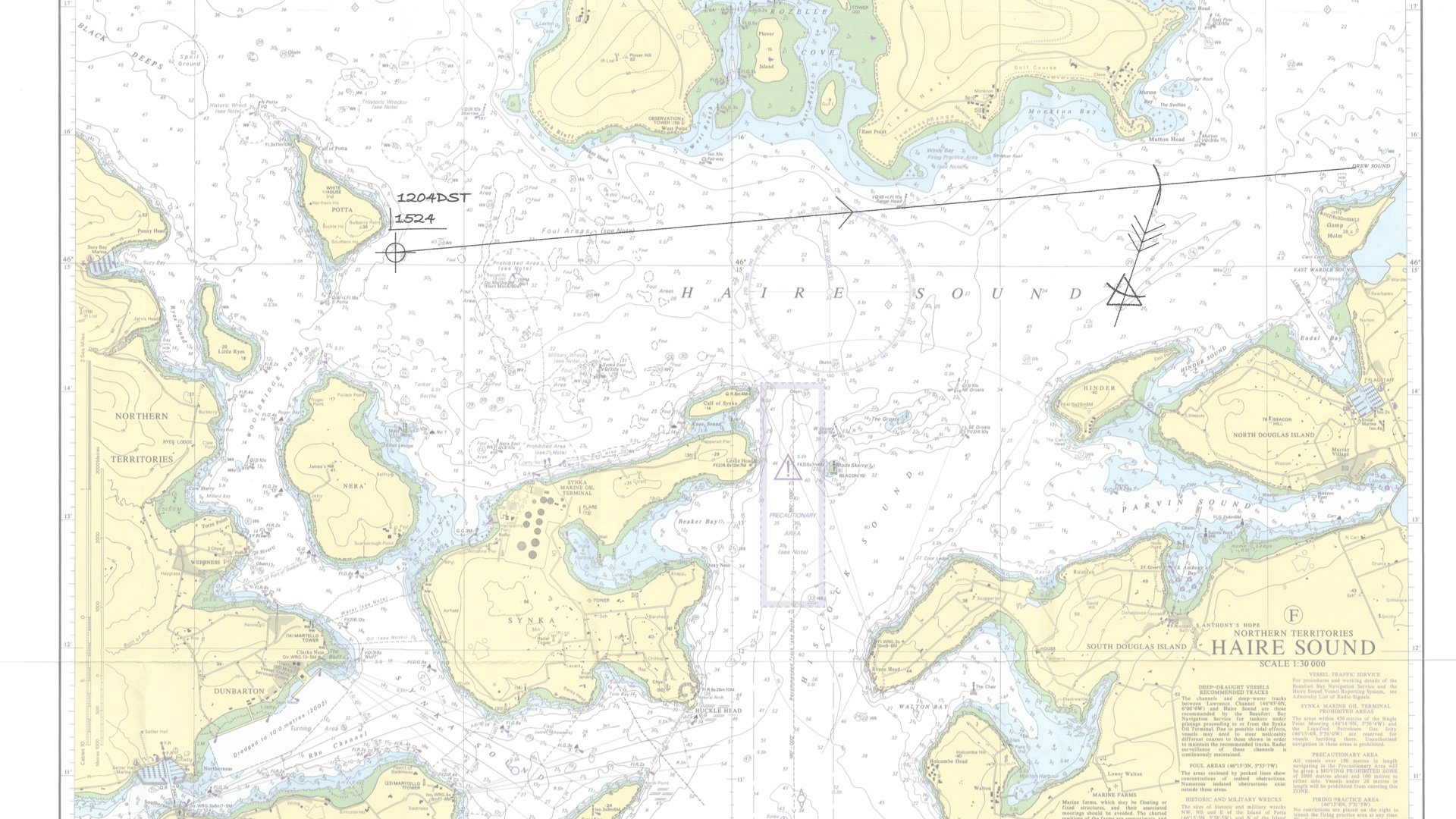
In traditional navigation, the EP is often marked on a chart with a triangle symbol, distinguishing it from a fix marked with a circle.
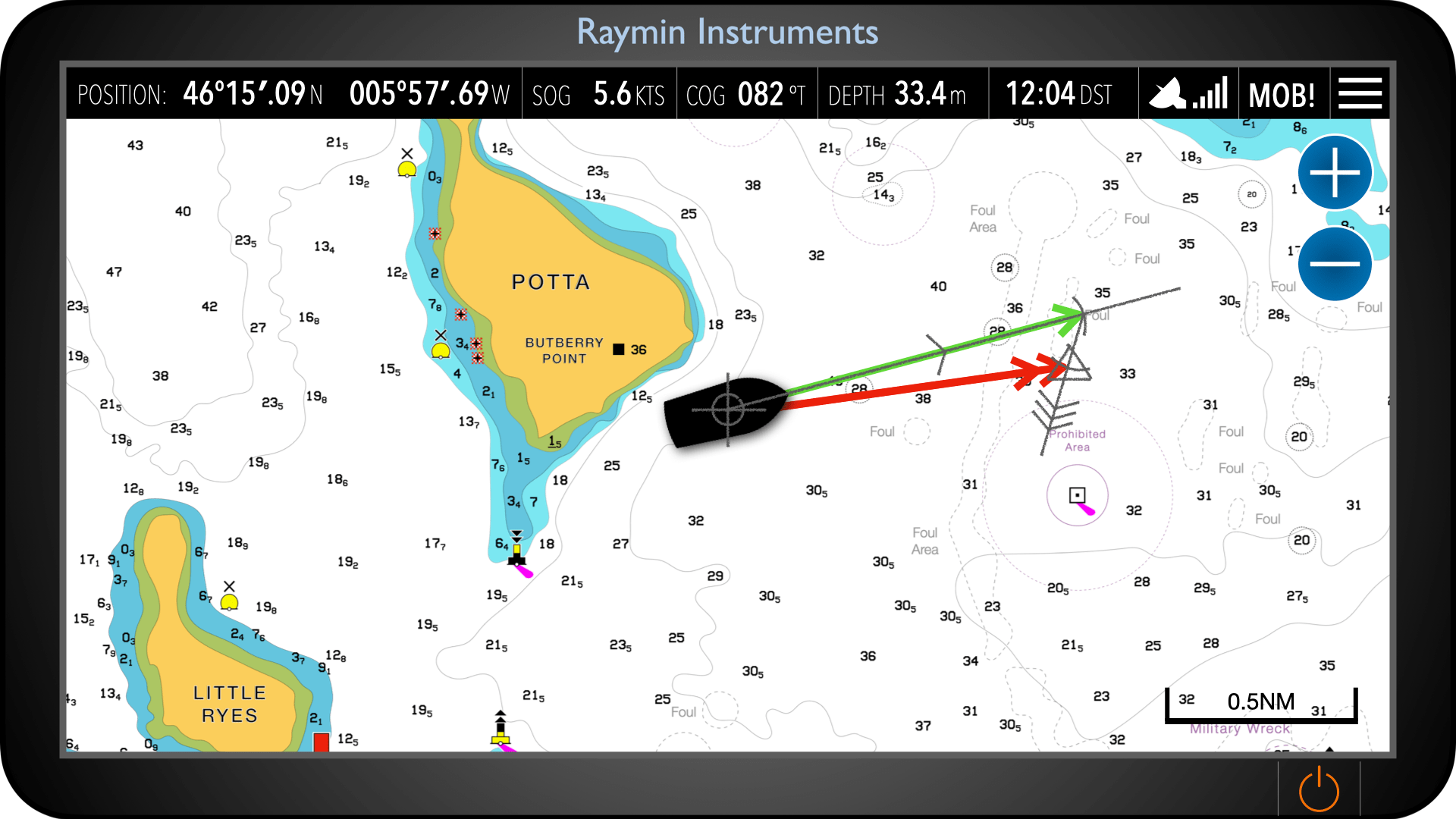
Traditional Chart Estimated Position on a chart verus a chart plotter
Traditionally, an estimated position was found by starting from a known position and advancing it using heading and speed made good, then applying the effects of tide and leeway.
On a modern chart plotter, the end of the COG vector represents the same concept. The vector is drawn from the vessel’s current position in the direction of course over ground, with its length based on a set time or distance. The position at the end of this vector is effectively an estimated position, as it shows where the vessel will be if the present conditions remain unchanged.