All our courses are engaging, interactive and fun! Whether formal training or simply looking to brush up, we take online learning to the next level.
An official record maintained aboard a vessel that documents the ship's daily activities, including navigational data, weather conditions, and significant events. A logbook, also known as a ship's log or deck log, is a crucial document on any vessel, whether it be a commercial ship, naval vessel, or recreational boat. It serves as a comprehensive...
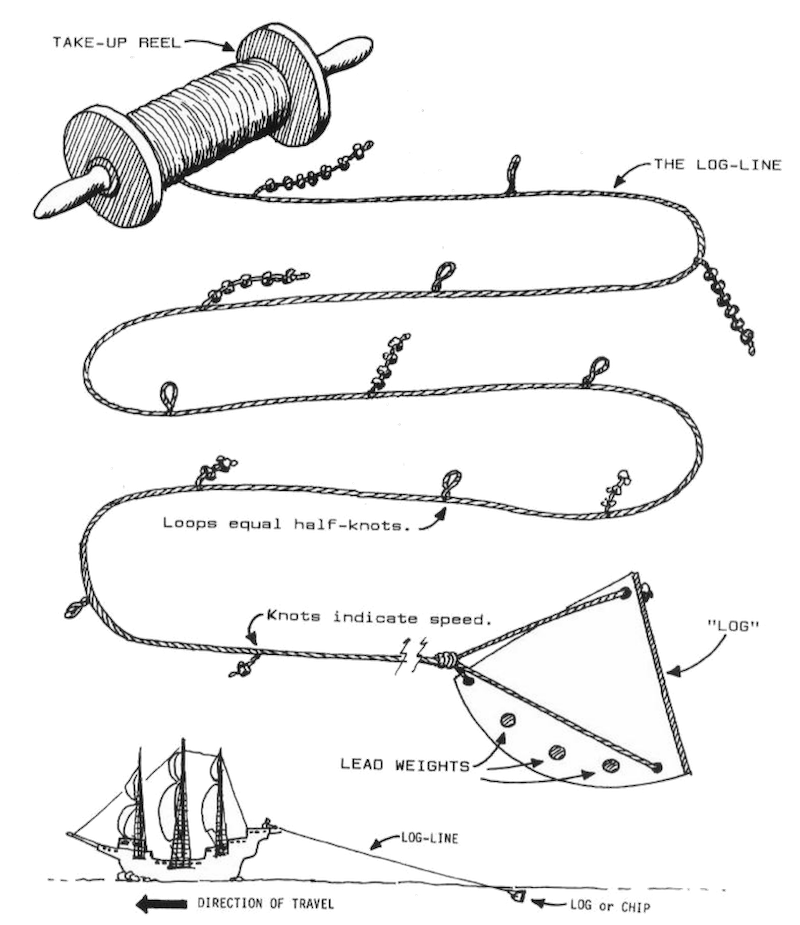
A device used historically by mariners to measure a vessel's speed through the water. The log line consists of a wooden board, known as the log, attached to a long, knotted rope. The log was thrown overboard and allowed to float behind the ship while the rope was paid out. Mariners would measure the vessel's...
The reading of distance travelled through the water usually taken every hour from the log and recorded in the deck log
The geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface, measured in degrees(°), minutes(') and seconds(") from the Prime Meridian. Longitude is one of the two key coordinates used in navigation and mapping to determine a specific location on the Earth's surface. The other is latitude. While latitude measures how...
A crew member assigned to maintain a continuous watch for potential hazards, other vessels, or navigational markers while at sea. A look-out is a critical role in maritime operations, ensuring the safety of the vessel and its crew by maintaining vigilance for any potential dangers or navigational aids. The look-out is typically stationed at a...
Navigational lines drawn on a chart, each representing a possible location of a vessel based on a single observation or measurement. A line of position (LOP) is a fundamental concept in marine navigation used to determine a vessel's location. It is a line on a nautical chart along which a ship is known to be...
A vessel loses way when she slows down and stops in the water
The lowest level that sea tides can reach under normal meteorological conditions, based on astronomical influences such as the gravitational pull of the moon and sun. Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) is a tidal datum used as a reference point for charting and navigation. It represents the lowest predicted tide level that can occur due to...
The marker in the compass which is aligned with the fore-and-aft line of the boat against which the course can be read off on the compass card
The leading edge, which is the part of the sail that faces the wind when the sail is set correctly. The luff of a sail is a critical part of sailboat dynamics and sail trim. It is the forward-most edge of the sail, running from the head (top) of the sail down to the tack...